Leveraging Colour Segmentation for Upper-Body Detection
| Home |
| Research |
| Publications |
| CV |
| Software |
Abstract
This paper presents an upper-body detection algorithm that extends classical shape-based detectors through the use of additional semantic colour segmentation cues. More precisely, candidate upper-body image patches produced by a base detector are soft-segmented using a multi-class probabilistic colour segmentation algorithm that leverages spatial as well as colour prior distributions for different semantic object regions (skin, hair, clothing, background). These multi-class soft segmentation maps are then classified as true or false upper-bodies. By further fusing the score of this latter classifier with the base detection score, the method shows a performance improvement on three different public datasets and using two different upper-body base detectors, demonstrating the complementarity of the contextual semantic colour segmentation and the base detector.Authors
Stefan Duffner, Idiap Research Institute, Switzerland / LIRIS, INSA de Lyon, France
Jean-Marc Odobez, Idiap Research Institute, Switzerland
Paper
S. Duffner and J.-M. Odobez, Leveraging Colour Segmentation for Upper-Body Detection, In Pattern Recognition, Vol. 47 (6), pp. 2222-2230, 2014.[bibtex] [djvu]
Datasets
We used three evaluation datasets:- INRIALite: a subset of the INRIA person dataset. This reduced dataset is composed of 145 images with only nearly frontal/rear people
- TA2: a set of 95 frames (containing 275 upper-bodies) extracted from the TA2 database
- Web: a set of 419 images, with 98 positive images containing 128 upper-bodies and 321 negative images
Note: these datasets can only be used for research purposes in the computer vision domain!
Annotation
The upper-body annotation can be downloaded here. Each line corresponds to a test image, having the form:filename number_of_upper_bodies top_left_x1 top_left_y1 width1 height1 top_left_x2 top_left_y2...Please cite the paper above if you use one of our datasets or our annotation!
Code
- The Calvin upper-body detector by Marcin Eichner and Vittorio Ferrari (ETH Zurich).
- The segmentation algorithm by Scheffler and Odobez (BMVC 2011). that our method is based on.
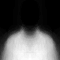
These are the spatial PIM prior models that have been used for the four classes: skin, hair, clothing, background. White represents a probability of 1.0 and black a probability of 0.0.



Results
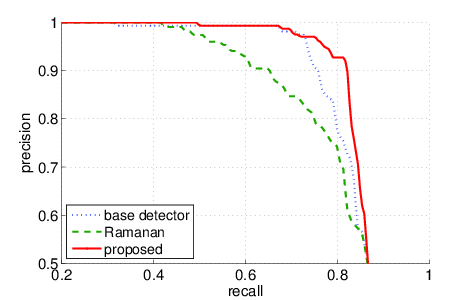
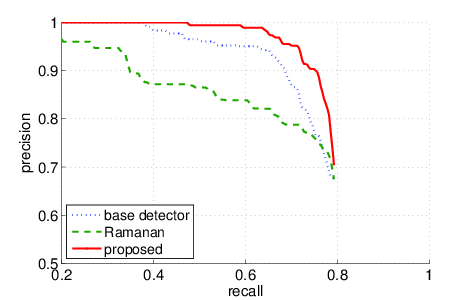
We compared the proposed approach with the base detector's performance (Calvin Detector: Eichner, Ferrari) and a similar approach to ours (D. Ramanan, Using segmentation to verify object hypotheses, CVPR, 2007). Here are the precision/recall curves:
INRIA Lite
TA2
Web

More results can be found in the paper.


